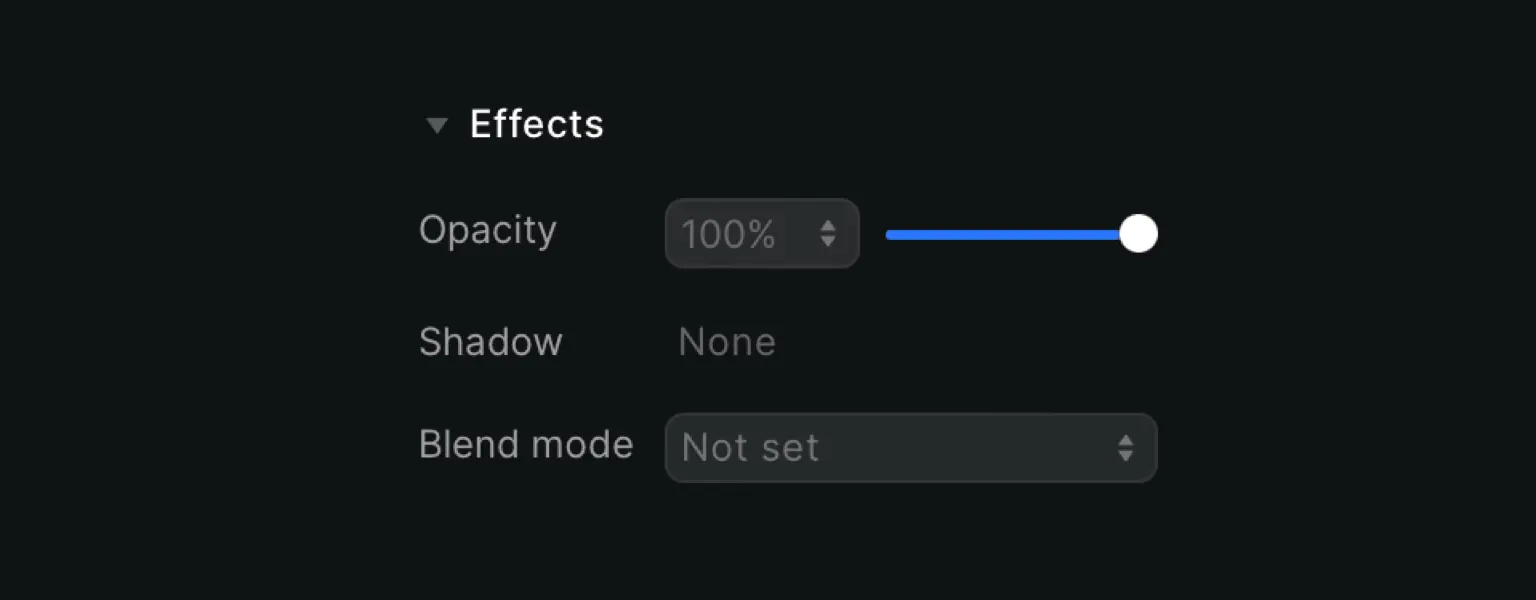
Opacity
Click the dropdown menu to choose a percentage or change the slider to set the correct number. With 100% opacity, the element is fully shown and 0% makes it disappear (as the element is transparent).
Shadow
Shadow works like a charm when you want to add depth to elements. You can pick from a shadow outside or inside the element.
If you go for Inside shadow, you can only pick the option base. This adds a light shadow border inside.
For Outside shadow, you can pick from a range of extra small to two times extra large shadows.
Click the trash can icon to delete the shadow effect.
Blend modes
Blend modes indicate how two layers blend with each other, and there are different types of effects you can choose from.
Before we dive into all modes, let’s clear up some terms:
Base color: Original color in an image.
Blend color: Color applied with the editing tool.
Luminosity: Glow or brightness.
Saturation: Intensity of a color. The higher, the more rich and vivid it is.
Hue: Pure colors, those that can be seen on the color wheel (primary and secondary).
Available blend modes
Normal: Default blend mode
Darken: Compares the base and blend colors and keeps the darkest of the two
Multiply: Always results in a darker color. Depending on the luminosity values of the blend layer, it may produce different darkening levels
Color burn: Darkens the colors and increases the contrast of the base colors (darker than multiply)
Lighten: Compares the base and blend colors and keeps the lightest of the two
Screen: Always results in a brighter color. Depending on the luminosity values of the blend layer, it may produce different brightening levels
Color dodge: Brightens the colors and decreases the contrast of the base colors (brighter than screen)
Overlay: Combination of multiply and screen, with the base layer shining through
Soft light: Very similar to overlay, but softer and subtler
Hard light: Combination of multiply and screen, using the brightness values to make its calculations
Difference: Uses the difference of the base and blend pixels as the resulting blend
Exclusion: Similar to difference but with a lower contrast level
Hue: Preserves the luminosity and saturation of the base pixels while adopting the hue of the blend pixels
Saturation: Preserves the luminosity and saturation of the base layer while adopting the saturation of the blend layer
Color: Preserves the luminosity of the base layer while adopting the hue and saturation of the blend layer
Luminosity: Preserves the hue and saturation of the base layer while adopting the luminosity of the blend layer











